Tenant application in ASP.NET Core
First of all, we have to know what a tenant is. Simply tenant is a customer. Meaning each customer is called a tenant.
Multi-tenant application in ASP.NET Core
Multi-tenancy is an architecture in which a single software application instance serves multiple customers.
In this case, a single software will manage multiple customer databases. But you have needed a tenant database for multiple tenants. This process is also called SaaS (Software as a Service).
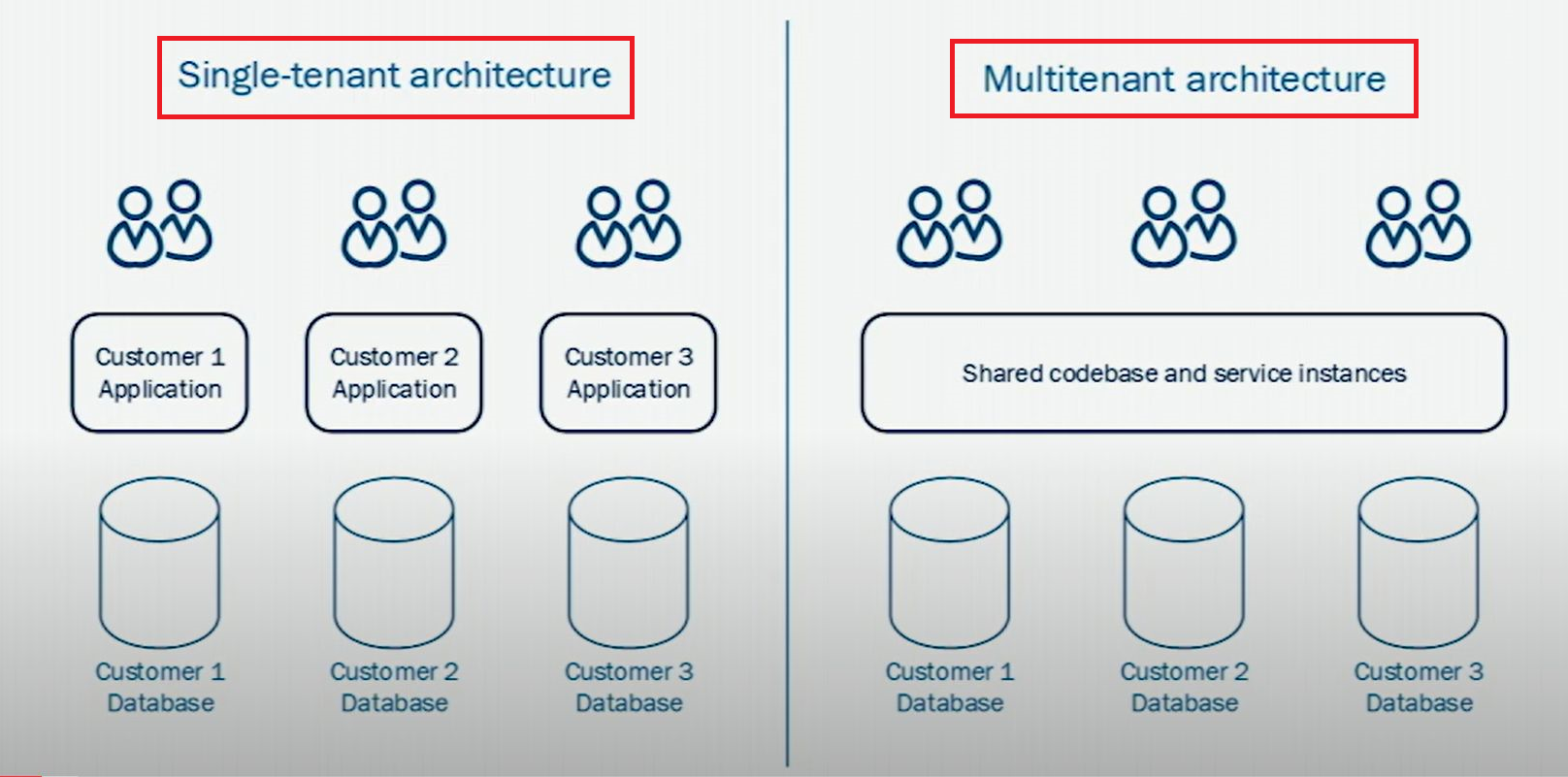
Moreover, you can also manage the software design style by multi-tenant architecture. In the case of a single tenant, every software-service instance has a separate database. Otherwise, in the case of multi-tenant only one software service instance, but there are multiple databases.
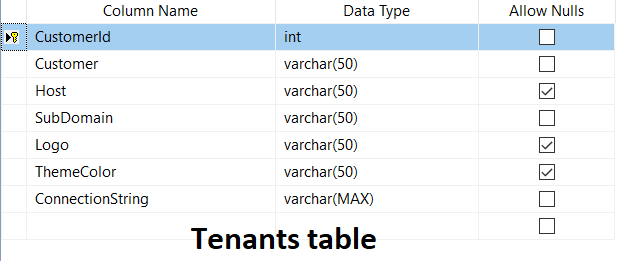
Tenant Database
I have to maintain a Tenant database to manage multiple customer Databases. I am using two tables, Like
![multi-tenant applications with ASP.NET Core]()
Application Database
Now I will add two application databases; these databases will access by a single web portal. Databases are like App-DB1 and App-DB2. Each database has one table, like Users.
![multi-tenant applications with ASP.NET Core]()
Create a Multi-tenant Application
Open visual studio editor 2022 and choose an ASP.Net Core Web App (MVC).
![multi-tenant applications with ASP.NET Core]()
![multi-tenant applications with ASP.NET Core]()
![multi-tenant applications with ASP.NET Core]()
Install SaasKit.Multitenancy
Go to the NuGet Package Manager and install the SaasKit.Multitenancypackage
![multi-tenant applications with ASP.NET Core]()
![multi-tenant applications with ASP.NET Core]()
This SaasKit.Multitenancy package will manage a multi-tenancy strategy.
Now add two classes, Tenants and TenantUsers.
Now add another class like TenantResolver. Here I will use TenantContext, which is come from SaasKit.Multitenancy package.
Service Registration
Go to the program file and register the Tenant class with TenantResolver class
Middleware Setup
This Tenant middleware will call with every HTTP request.
Install Entity Framework Core
I will useEFCore ORM to access SQL Database. So, we need to install the required packages. Like
![multi-tenant applications with ASP.NET Core]()
After installing these three packages, I will add Two database contexts. One context is for Tenant-Database and another for App-Database. Like
![multi-tenant applications with ASP.NET Core]()
TenantDBConnection
Now add Signin and Users class in the Models folder. Like
DB context Implementation
Now time to implement Db contexts. Like
Add Services
I have used two services for this application. One for tenant operation and another for application operation. Like
![multi-tenant applications with ASP.NET Core]()
- GetTenantBySubDomain()- This method will return a tenant by sub-domain.
- GetTenantByEmail ()- This method will return a tenant by email.
- GetTenantByEmail()- Here, this method will return a valid URL with a sub-domain.
- Signin()- This method is used to sign in to this portal. It will return a URL as a string.
TenantResolver implementation
This resolver will resolve a multitenant strategy in each HTTP request. If the tenant is valid, then the HTTP request will execute else. The application will show an error. Here I am checking the sub-domain in each request. So, if the sub-domain exists and is valid, the app will work fine; otherwise shows an error. This is a demo and my logic and implementation so anyone can implement his logic.
Controller Implementation
Now add a Signin action in HomeController for view. Like,
Also, add Signin Post Action for Signin. Like,
The detail I have implemented the into the source code. So don't worry; I have provided the source file.
Logout action
Go to the master _Layout.cshtml page and inject the Tenant class to access the required property. I will use the ThemeColor property to change the theme according to the user's colour. Like,
Same as the index and privacy files. I will use the Customer name from the tenant class. Like
Run the project and sign in by different users. Like
First, for the red user
![multi-tenant applications with ASP.NET Core]()
and second for green user
![multi-tenant applications with ASP.NET Core]()